Understanding Gum Surgeries: Different Types and the Gum Grafting Procedure
Maintaining healthy gums is crucial for overall oral health, but sometimes, gum disease or other conditions may necessitate surgical intervention. Gum surgeries can address various issues, from gum recession to severe periodontal disease. In this blog, we’ll explore the different types of gum surgeries, focusing particularly on gum grafting operations.
Types of Gum Surgeries
- Gingivectomy
A gingivectomy is performed to remove and reshape loose, diseased gum tissue. This procedure is often used to treat gum disease and can help reduce pockets between the teeth and gums where bacteria can accumulate.
- Gingivoplasty
Gingivoplasty involves reshaping healthy gum tissue for cosmetic or functional reasons. It is often performed alongside a gingivectomy or as a standalone procedure to create a more aesthetically pleasing gum line.
- Flap Surgery (Periodontal Pocket Reduction)
Flap surgery is used to treat advanced periodontal disease. During this procedure, the gums are lifted back to remove tartar and bacteria from the roots of the teeth. The gums are then sutured back in place to fit more snugly around the teeth, reducing pocket depth and making it easier to maintain oral hygiene.
- Crown Lengthening
Crown lengthening is a surgical procedure that removes excess gum tissue and bone to expose more of a tooth’s surface. This can be necessary for restorative dental work, such as placing a crown, or for cosmetic reasons to correct a “gummy” smile.
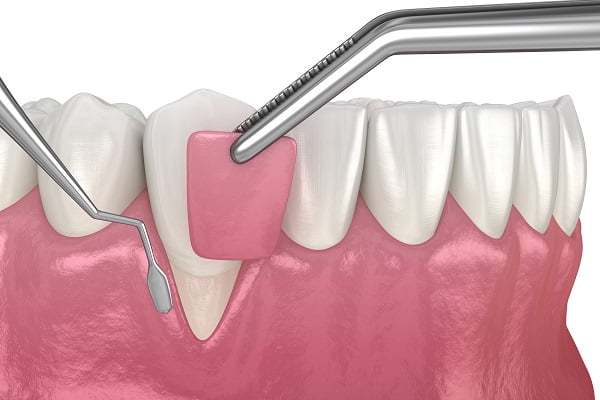
- Gum Grafting
Gum grafting is a common procedure used to treat gum recession. This condition can expose the roots of the teeth, leading to increased sensitivity and a higher risk of decay and damage. Gum grafting helps to cover exposed roots, reduce sensitivity, and improve the appearance of the gum line.
Gum Grafting: An In-Depth Look
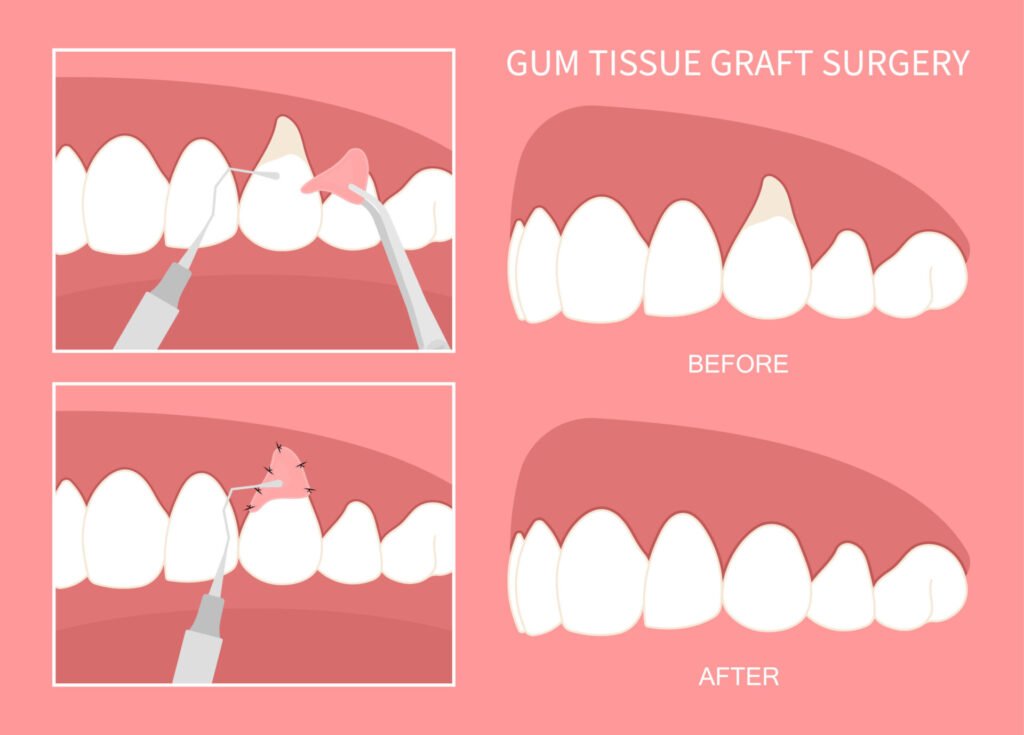
Gum grafting, also known as gingival grafting, involves taking gum tissue from one area of the mouth and attaching it to another area where gum tissue is lacking. Here’s a detailed overview of the gum grafting procedure:
Types of Gum Grafts
- Connective Tissue Grafts
This is the most common type of gum graft. It involves creating a flap in the roof of the mouth (palate) and removing a small piece of connective tissue from beneath the flap. This tissue is then stitched to the area of gum recession. The flap in the palate is then sutured back.
- Free Gingival Grafts
In this procedure, tissue is taken directly from the roof of the mouth without creating a flap. This method is often used for patients who have thin gums and need additional tissue to prevent further recession.
- Pedicle Grafts
For pedicle grafts, the gum tissue is taken from an area adjacent to the tooth needing repair. A flap, called a pedicle, is partially cut away so that one edge remains attached. The flap is then pulled over or down to cover the exposed root and stitched into place.
The Procedure
- Consultation and Preparation: The process begins with a thorough examination by a periodontist. X-rays and other diagnostic tools may be used to assess the extent of gum recession and plan the procedure.
- Anesthesia: Local anesthesia is administered to numb the area where the graft will be placed and where the tissue will be harvested.
- Tissue Harvesting: Depending on the type of graft, tissue is harvested from the roof of the mouth or nearby gums.
- Grafting: The harvested tissue is carefully sutured to the area experiencing gum recession.
- Post-Procedure Care: Patients will receive instructions on how to care for their gums during the healing process. This typically includes avoiding certain foods, maintaining good oral hygiene, and possibly using a special mouth rinse to prevent infection.
Recovery and Results
Recovery from gum grafting generally takes one to two weeks. Patients might experience some discomfort and swelling, which can be managed with prescribed pain relievers and anti-inflammatory medications. It’s essential to follow post-operative care instructions closely to ensure proper healing and optimal results.
The results of gum grafting can significantly improve oral health by covering exposed roots, reducing sensitivity, and creating a more uniform and aesthetically pleasing gum line. This procedure not only enhances the appearance of your smile but also protects the teeth from further damage and decay.